|
Main Index
Audio CD Input
Auxiliary Input
dBpowerAMP Music Converter
Compression Codec
Settings
mp3
(Lame) Compression Settings
Wave
Compression Settings
dBpowerAMP licenses various Patents from Thompson for mp3 encoding &
decoding.
Lame is the King of mp3 encoders, reasonably fast and giving possibly the
highest quality, continually developed, dBpowerAMP ships with the latest
version. A license is required for mp3 encoding, the reason for a license
is explained.
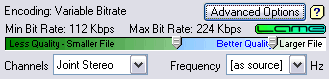
mp3 (Lame) Compression
Options
The green bar represents the Bitrate
bar, this is the quality of the resulting mp3 file, higher bit rates files
are of a higher quality than lower bit rate files. Some presets
(already defined modes) handle the quality and bitrate so when a preset is
selected the bitrate pointer(s) might disappear.
Optimum Settings
To quickly set lame to its
best - set both Channels and Frequency to [as source] and click Advanced
Options, under Presets select one of the Alt presets such as
ALT Preset Standard. It is the ALT presets that give the highest quality
for file size, there are a variety to choose from that alter the final
size and quality. It should be noted, most Alt presets use VBR
(see below), your mp3 player (if an older portable) might not be
compatible with VBR encoded files, the various ALT presets are:
-
Alt Preset Standard
results in an audio file of high quality and of a reasonable size,
-
Alt Preset Fast
Standard as above, but sacrificing very slight quality for
a higher speed of compression,
-
Alt Preset Extreme of
a higher quality and larger ending file size than Standard,
-
Alt Preset Insane
for those who want the highest quality mp3 possible, bitrates will
be around 320Kbps,
-
Alt Preset CBR
when a fixed bitrate is used throughout compression (for players
incompatible with VBR),
-
Alt Preset VBR
user specifies an average bit rate,
All Settings
Green Bitrate Scale: when
being used for constant, or average bitrate (see below) there is one
pointer - clicking the left mouse button on the scale sets the bitrate.
For Variable bitrates there are two pointers, a minimum bitrate (set
with the left mouse button) and a maximum bitrate (right mouse button).
Frequency - number of
samples per second to be encoded, [as source] will set the final
frequency to the source frequency (44.1KHz for Audio CDs).
Channels
- [as source] set the channels to
that of the source (2 for Audio CDs), if 2 channels then Joint
Stereo (preferred 2 channel option) is used.
- Stereo - two separate audio
channels.
- Mono a recording with only a
single channel of information. A question that is often asked Why
is my 128kbps encoded Mono file, not half the size as a 128kbps
encoded Stereo file? The answer is simple, to keep the Kbps rate
constant, the mono file is encoded at twice the quality rate as the
stereo file (Kbps measurement is for the whole recording regardless
of the number of channels, so Per Channel Kbps = Kbps / Number of
Channels).
- Joint Stereo - luckily for
stereo compression sound on the left channel is very similar to
sound on the right channel, Joint Stereo takes advantage of this
similarity to use the savings on the 2nd channel to give higher
quality compression.
Advanced Options
Clicking Advanced Options
offers:

Preset Quality there
are dedicated people who have done all the work in determining settings
for various qualities, each of the ALT presets are described under
optimum settings (above). Many of these presets over-ride certain other
settings, so don't be surprised if you cannot alter a bitrate after
setting a preset.
Encoding - mp3
files fall into these distinct types:
-
Constant Bit Rate (CBR),
a constant bit rate is used throughout the encoding process, so a
128Kbps audio file of 60 seconds will always be around 960KB in
size (128 * 60) / 8,
-
Variable Bit Rate
(VBR). Mp3 files are made up from 100's of small audio chunks,
called frames. Whilst encoding VBR files the encoder decides which
bit rate to use for each frame. Bit rates can drop down to lower
value when it is warranted (if there is not much sound going on),
and switch up to a higher bit rate when required. VBR files are
great when a compromise between file size, and quality has to be
made. VBR Options - a Minimum Bit Rate and a Maximum
Bit Rate are specified by clicking the left and right mouse
buttons on the green bit scale. Quality 'Low ---- High'
controls the quality factor for VBR (higher quality larger files).
Disable Bit Reservoir stops the
carrying over of bit reservoir between frames, resulting in less
space for audio (slightly lower sound quality), should only be used if audio
player requires (very few should),
-
Average Bit Rate
a little like VBR except with VBR the end file size is not known
(could be small, could be big), ABR is VBR with known end file
size, it works by regulating how variable the compression is, so
at the end of the compressing the average is roughly the value
specified.
Set Bits
-
Copyright marks
the mp3 file as containing copyright material,
-
Original marks
the mp3 file as an original file (not a copy),
-
Private - the
mp3 is private.
Write CRC Checksums
adds a checksum to each frame, so the decoder can tell if it has become
corrupted, very few audio players use checksums.
mp3 dMC Configuration
Options
From dMC Configuration (start
>> programs >> dbpoweramp music converter >>
configuration) Options reveals additional codec options:
CRC Errors:
certain mp3 files are encoded with CRC checks within each frame,
this option can set the decoder to skip a frame with errors.
Decode To: sets
the output resolution when decoding a mp3 file, it is recommended
the default 16 Bit (dither) is used as not to create compatibility
problems with other codecs.
Advanced Tagging Configuration
From dMC Configuration (start
>> programs >> dbpoweramp music converter >>
configuration) ID Tag Options reveals tagging options, these
options are only used when creating new tags, not editing existing:
Mp3
Tag Creation mp3 files can
have many different types of ID3 tags, they are:
definitions: Element - title
of tag item such as Artist, Data - tag value
such as Madonna
- ID3v1 which is limited to fixed
Element names and about 30 characters per Data item,
- ID3v2 writes tags at the beginning of
the file which results in slower tag writing, ID3v2 has many fixed
Element names, data values can be any length and Unicode,
- APEv2 a modern tagging format, Unicode
characters, allows any Element and any length Data items,
The preferred tagging type is ID3v2
most programs are compatible with ID3v2, if you are using characters
outside of normal ANSI (a-z) consider enabling Write ID3v2
Unicode as this will allow the correct writing of international
ID Tags (especially Far Eastern Tags).
Write ID3v1 Version, ID3v1 has two
subversions: ID3v1.0 and ID3v1.1, the difference is v1.1 shortens
the comment field by 1 character to store off a track number.
ID3v1 UTF8 Read reads ID3v1 tags that have been encoded as UTF8
(Unicode)
ID3v1 UTF8 Write writes ID3v1 fields as UTF8, not recommended for
compatibility reasons,
Write ID3v2 Unicode will write UTF-16 characters, not all
programs will be able to read Unicode ID3v2 files, check compatibility,
Write ID3v2 Version there are many sub versions to ID3v2, can be
set to an older version if an older program requires,
 Compression
Compression
 Jump to Top Jump to Top
 Wave Settings
Wave Settings 
|
|
![]()